It’s easy to overlook units of measurement in Blender, but trust me, they’re more important than you might think. Especially for projects that aim for real-world scale and physical accuracy, using the wrong units or scaling things incorrectly can trigger a domino effect of problems.
For example, if you’re creating a scene with real-world dimensions but your units are set to millimeters, your lighting might appear overly bright or cast unrealistic shadows. Similarly, simulations like cloth or fluid dynamics rely on accurate scale and units to behave as expected. Even texturing can be affected, with materials potentially appearing stretched or distorted if the scale is off.
If you need to adjust your units, Blender offers a range of systems to choose from, including Metric, Imperial, and Blender Units.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to change the units of measurement in Blender 3D.
How to Change Units in Blender
1. Open Blender and Go to Scene Properties Panel

Start by opening Blender. In the Properties Editor located on the right side of the interface, click the icon that resembles a cone and a sphere to access Scene Properties.
2. Expand the Units Tab

Scroll down to find the Units tab. Click on it to expand the unit system settings.
3. Select the Desired Unit System

Here, you can choose from different unit systems:
- Metric: Suitable for most applications outside the United States, this includes meters, centimeters, millimeters, etc.
- Imperial: Ideal for users in the United States, this includes feet, inches, etc.
- None: Blender Units, which are arbitrary units used solely within Blender.
4. Adjust Specific Settings

After you’ve picked your measurement system (like metric or imperial), you get to choose the individual units. For example, if you’re using the metric system, you could choose ‘kilometers’, ‘meters’, and so on. These units will be used everywhere in Blender, so think about the overall size of your scene.
Various measurements are:
- Rotation: Angle measurement, you can use either degrees or radians.
- Length: This can be meters, feet, etc.
- Mass: You can set this to kilograms, pounds, etc.
- Time: Default is in seconds, but you can adjust it to other time units.
- Temperature: Default is in Celsius but can be set to Fahrenheit or Kelvin.
Unit Scale: This option lets you fine-tune the size of your units. Imagine you’re working on a miniature model-you might want to set the scale to 0.1 or 0.01. For those epic, large-scale scenes, you could use 10 or 100.
5. Display Units in the 3D Viewport
Blender offers a variety of ways to display measurements, catering to different needs and workflows. Here’s a breakdown of the common methods:
A. Display Measurement using Measure Tool

To display measurements in Blender using the Measure tool, follow these steps:
- Activate the Measure Tool: You can find it in the toolbar. It looks like a ruler or angle ruler.
- Create Rulers: Click and drag in the viewport to define the start and end points of the ruler. You can add multiple rulers.
- Measure Distances and Angles: Drag either end of the ruler to move it. Holding
Ctrlwhile moving enables snapping to edges and vertices. HoldingShiftwhile moving lets you measure the distance between faces. - Convert to Protractor: Click on the midpoint of a ruler to convert it to a protractor. The midpoint can then be dragged just like the endpoints.
Keep in mind that these measurements only show up when the Measure tool is active.
B. Display Edge Length

To display edge lengths in Blender, follow these steps:
- Go to Edit Mode: Select your object and press
Tabto enter Edit Mode. - Enable Edge Lengths: In the 3D Viewport, click the ‘Overlay’ button, which looks like a small upside-down triangle (located in the top-right corner of the viewport).
- Activate Measurements: In the Overlay options, check the box next to ‘Edge Length’. This will display the lengths of the selected edges.
You should now see the measurements of the edges directly in the viewport. This is super useful for quickly checking dimensions while you’re modeling.
Important Notes:
Apply Scale: If you’ve already started modeling and then change your units, remember to apply the scale of your objects (Object > Apply > Scale) to prevent unexpected distortions.
Real-World Scale: Pay attention to the unit scale to maintain realistic proportions, especially when importing models from different sources.
Adaptive Measurement
Adaptive measurement in Blender is a really cool feature that lets you change how units are displayed in your viewport. It basically means the units you see on screen adjust themselves based on the size of the object you’re working with.
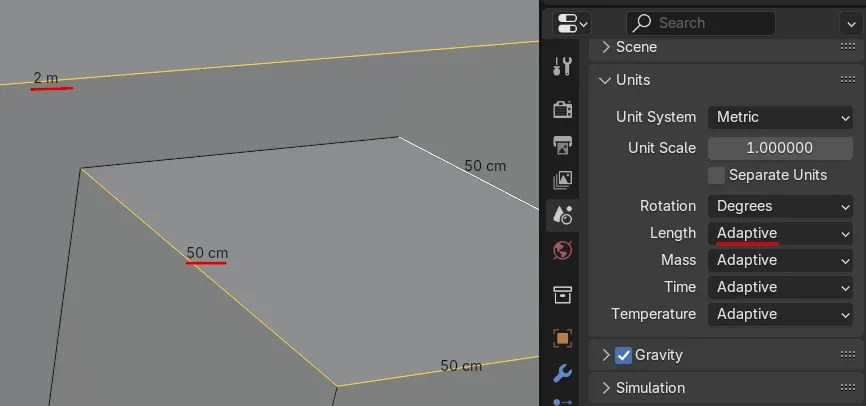
Imagine you’re modeling a whole city in Blender. If you used the same units for everything, you might end up with tiny buildings measured in kilometers or huge roads measured in millimeters. That would be pretty confusing, right? Adaptive measurement solves this by automatically switching to the most appropriate unit. So, your buildings might be measured in meters, while the distances between them are shown in kilometers. This keeps everything nice and tidy, no matter the scale of your project.
To turn on adaptive measurement, just go to the “Scene Properties” tab and look for the “Units” section. There, you’ll find an option called “Adaptive.” Once you’ve enabled it, you can also customize how it works by setting the scale and precision.
Practical Uses of Units in Blender
Choosing the right units in Blender can make a huge difference depending on what you’re creating. In architectural visualization, for example, using real-world units like meters or feet ensures that your 3D model accurately reflects the intended dimensions of a building or space. This is crucial for things like creating realistic 3d floor plans, walkthroughs or planning furniture layouts.

Similarly, in product design and 3d printing, precise measurements in millimeters or inches guarantee a perfect fit. For example, designing a phone case requires exact measurements to ensure it fits correctly. Getting the units right can make the difference between a successful product and a costly mistake.

For game development, different game engines and platforms often have their own preferred unit systems. By setting up Blender to use the same units, you can avoid potential issues when importing your models. This ensures that everything looks and behaves as expected within the game environment, streamlining your workflow and preventing headaches down the line.
Conclusion
While it’s true that many projects in Blender benefit from setting the correct units, it’s not always a critical step. For simple scenes or those not relying on real-world scale, precise unit configuration might not be necessary. However, when creating projects where accurate lighting, simulations, or texturing are crucial, defining the right units early on can prevent unexpected issues and ensure consistency. By matching your scene’s units to your project’s needs, you can achieve more predictable results and a final product that aligns with your creative vision. So, while not always mandatory, consider the scope and requirements of your project before diving into detailed unit settings.
Takeaways:
- Location: Properties Panel > Scene Tab > Units
- Options: Metric or Imperial
- Best Practice: Set units BEFORE modeling
- Pro Tip: Use the measuring tool to verify dimensions
Frequently Asked Questions – Units of Measurements in Blender
In Blender, you have the flexibility to work with different units of measurement to best suit your project’s needs. Here are the main units of measurement available:
1. None (Blender Units): Arbitrary units, not based on real-world measurements.
2. Metric: Uses meters, centimeters, millimeters, etc., ideal for precise, real-world scaling.
3. Imperial: Uses feet, inches, etc., suitable for projects requiring US customary units.
You can customize these for length, angles, and time to suit your project needs.
By default, Blender uses the Metric system with meters (m) as the base unit of measurement. However, you can easily change the unit settings to use millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), or any other metric units depending on your project requirements.
First, open Blender and go to the properties panel on the right side. In this panel, locate the Scene Properties tab, represented by an icon that looks like a cone, sphere, and cylinder stacked together. Click on the units dropdown; by default, Metric will be the unit system.
Next, set the unit to millimeters. In the Length dropdown, select “Millimeters (mm).” This ensures that all measurements in your scene are now displayed in millimeters. Additionally, you can adjust the display precision if necessary, allowing you to define how many decimal places are shown for measurements.

